中国海洋湖沼学会主办。
文章信息
- 梁玉波, 李冬梅, 姚敬元, 金薇, 宫长宝, 刘仁沿. 2019.
- LIANG Yu-Bo, LI Dong-Mei, YAO Jing-Yuan, JIN Wei, GONG Chang-Bao, LIU Ren-Yan. 2019.
- 中国近海藻毒素及有毒微藻产毒原因种调查研究进展
- PROGRESSES IN INVESTIGATION AND RESEARCH ON PHYCOTOXINS AND TOXIC MICROALGAES IN THE COASTAL WATERS OF CHINA
- 海洋与湖沼, 50(3): 511-524
- Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 50(3): 511-524.
- http://dx.doi.org/10.11693/hyhz20181000233
文章历史
-
收稿日期:2018-10-04
收修改稿日期:2018-10-21
2. 大连市藻毒素重点实验室 大连 116023
2. Dalian Phycotoxins Key Laboratory, Dalian 116023, China
海洋藻毒素主要是由海洋有毒微藻产生的活性物质, 贝类等摄食了有毒微藻, 就会将毒素富集于体内, 人类食用了藻毒素污染的贝类等海产品就会中毒甚至死亡。按中毒症状, 藻毒素分为麻痹性贝类毒素(Paralytic Shellfish Poisoning, PSP)、腹泻性贝类毒素(Diarrhetic Shellfish Poisoning, DSP)、神经性贝类毒素(Neurotoxic Shellfish Poisoning, NSP)、失忆性贝类毒素(Amnesic Shellfish Poisoning, ASP)和西加鱼毒(Ciguatera Fish Poisoning, CFP)。2004年, 联合国粮农组织(Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, FAO)、联合国政府间海洋学委会(Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission, IOC)和世界健康组织(Word Health Organization, WHO), 按化学结构将贝类毒素分为8组, 即石房蛤毒素组(saxitoxin, STX)、软骨藻酸组(domoic acid, DA)、大田软海绵酸毒素组(okadaic acid, OA)、氮杂螺环毒素组(azaspiracid, AZA)、短裸甲藻毒素组(brevetoxin, BTX)、蛤毒素组(pecenotoxin, PTX)、虾夷扇贝毒素组(yessotoxin, YTX)和环亚胺类毒素(cyclic imine, CI), 除STX和DA为水溶性的, 其他毒素均为脂溶性的, 具热稳定性, 易溶解于甲醇和乙醚等有机试剂。
目前, 我国是世界上海产品生产和消费第一大国, 近海有毒赤潮频发。本文通过对我国近海藻毒素污染状况及有毒微藻进行系统综述分析, 为促进我国海洋生态环境保护和海产品食用安全, 提供可靠科学的依据。
1 我国近海麻痹性贝类毒素污染状况及其产毒微藻 1.1 我国近海麻痹性贝类毒素污染状况早在1978年, 就开始了长江口海域麻痹性贝类毒素的调查(林燕棠等, 1999)。尔后, 在全国其他海域相继开展了较多的调查研究, 2006—2015年, 进行了全国近岸海域麻痹性贝类毒素的系统性调查, 为全面评估我国近岸海域毒素污染状况, 提供了可靠的数据。
1.1.1 黄海1996年首次在黄海连云港海域检出麻痹性贝类毒素(Zhou et al, 1999), 2004—2015年, 黄海近岸海域麻痹性贝类毒素污染比较严重, 尤其是2003—2008年, 北黄海虾夷扇贝体中麻痹性贝类毒素污染较重, 消化腺中毒素可达65140µg/kg; 在每年4—6月份为毒素污染高峰期(夏远征等, 2010)。1991—2003年, 连云港的织纹螺体中的麻痹性贝类毒素污染严重, 可高达220000µg/kg(表 1), 已引发多起中毒事件(林祥田等, 2005)。
| 海域 | 年份 | 样本数(个) | 检出率(%) | 超标率(%) | 最高含量 (µg/kg) |
参考文献 |
| 青岛 | 1994—1996 | 805 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 李伟才等, 2000 |
| 烟台 | 1995—1997 | 429 | 0.2 | 0 | 0 | 李伟才等, 2000 |
| 大连、青岛、赣榆等 | 1996 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 林燕棠等, 2001 |
| 1999 | 16 | 8 | 0 | 460 | 林燕棠等, 2001 | |
| 连云港 | 1996—1997 | 23 | 4.3 | 0 | 70 | Zhou et al, 1999 |
| 黄海近岸 | 1997 | 18 | 5.5 | 5.5 | 1152 | 关春江等, 1999 |
| 烟台 | 1997 | 21 | 9.5 | 4.7 | 1330 | Zhou et al, 1999 |
| 黄渤 | 2003—2005 | 97 | 6.1 | 2.1 | 801 | 孔凡洲等, 2007 |
| 大连黄海 | 2003—2004 | 14 | 57.1 | 7.1 | 3314 | 江天久等, 2007 |
| 连云港 | 2004 | 8 | 100 | 100 | 220000 | 林祥田等, 2005 |
| 大连黄海 | 2007—2008 | 72 | 70.8 | 26.3 | 65140 | 夏远征等, 2010 |
| 大连大窑湾* | 2007—2008 | 24 | 100 | 33.3 | 5628 | 韩华等, 2012 |
| 大连大窑湾 | 2007—2008 | 24 | 75 | 25 | 1847 | 韩华等, 2012 |
| 北黄海** | 2007—2008 | 4 | 100 | 100 | 8430 | Li et al, 2012a |
| 大连 | 2007—2008 | 54 | 48.1 | 2041 | 宋普江等, 2011 | |
| 大连 | 2007—2008 | 21 | 90.5 | 47.6 | 4291 | 杜克梅等, 2013a |
| 江苏 | 2007—2008 | 21 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 杜克梅等, 2013a |
| 山东蓬莱 | 2007—2008 | 19 | 5.3 | 0 | 277 | 杜克梅等, 2013a |
| 北黄海* | 2006—2008 | 120 | 45.8 | 4.2 | 1138 | 梁玉波, 2012 |
| 北黄海 | 2006—2008 | 120 | 35.8 | 3.3 | 1139 | 梁玉波, 2012 |
| 南黄海* | 2006—2008 | 122 | 26.2 | 4.9 | 1567 | 梁玉波, 2012 |
| 南黄海 | 2006—2008 | 122 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 341 | 梁玉波, 2012 |
| 北黄海* | 2013—2015 | 273 | 74 | 21.2 | 98996 | 本文 |
| 南黄海* | 2013—2015 | 100 | 64 | 17 | 453154 | 本文 |
| 平均值 | 38.2 | 18.8 | 36300 | |||
| 注: *为液相色谱法, **为液相色谱-质谱法, 其他为小鼠生物法 | ||||||
1996年首次在渤海天津海域检出麻痹性贝类毒素(林燕棠等, 1999), 2006—2016年, 渤海近岸海域麻痹性贝类毒素逐年升高, 2015年夏季莱州湾的菲律宾蛤仔体中毒素可达60573µg/kg; 2016年春季, 秦皇岛海域的紫贻贝体中麻痹性贝类毒素可达40561µg/kg(表 2)。
| 海域 | 年份 | 样本数(个) | 检出率(%) | 超标率(%) | 最高含量(µg/kg) | 参考文献 |
| 秦皇岛 | 1993—1997 | 392 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 李伟才等, 2000 |
| 天津、莱州、营口 | 1996 | 16 | 18.8 | 0 | 460 | 林燕棠等, 1999 |
| 1999 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 林燕棠等, 2001 | |
| 渤海 | 1997 | 20 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 关春江等, 1999 |
| 渤海 | 2003—2005 | 57 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 孔凡洲等, 2007 |
| 渤海* | 2006—2008 | 133 | 31.5 | 4.5 | 1741 | 梁玉波, 2012 |
| 渤海 | 2006—2008 | 133 | 8.333333 | 0 | 432 | 梁玉波, 2012 |
| 渤海* | 2013—2015 | 186 | 73.6 | 15.6 | 60573 | Liu et al, 2017a, 本文 |
| 秦皇岛* | 2016 | 10758 | Ding et al, 2017 | |||
| *秦皇岛* | 2016 | 15 | 53.3 | 26.7 | 39209 | 本文 |
| 秦皇岛 | 2016 | 15 | 53.3 | 26.7 | 40561 | 本文 |
| 平均值 | 23.9 | 7.4 | 14298 | |||
| 注: *为液相色谱法, **为液相色谱-串联质谱法, 其他为小鼠生物法 | ||||||
1996年首次在宁波纺纹螺体中检出麻痹性贝类毒素, 至2003年每年均有毒素检出, 含量可高达97344µg/kg(于梅等, 2004)。2015年夏季, 厦门竹蛏体内麻痹性贝类毒素含量可达23793µg/kg; 2017年福建近海贻贝体中毒素可高达34146µg/kg。近几年来, 福建近海麻痹性贝类毒素污染呈明显加重趋势(表 3)。
| 海域 | 年份 | 样本数(个) | 检出率(%) | 超标率(%) | 最高含量(µg/kg) | 参考文献 |
| 长江口 | 1978 | 33300 | 林燕棠等, 1999 | |||
| 宁波 | 1986—2003 | 127 | 100 | 48.8 | 97344 | 于梅等, 2004 |
| 舟山 | 1996—1997 | 16 | 6.3 | 0 | 10 | Zhou et al, 1999 |
| 福建沿岸 | 1993—1996 | 53 | 3.8 | 李伟才等, 2000 | ||
| 宁波、温州、厦门等 | 1996 | 32 | 10.3 | 0 | 350 | 林燕棠等, 2001 |
| 1997 | 17 | 5.5 | 0 | 440 | 林燕棠等, 2001 | |
| 舟山 | 2002 | 22 | 13.6 | 0 | 306 | 江天久等, 2003 |
| 厦门海域 | 2002—2003 | 53 | 7.5 | 0 | 400 | 王雪虹等, 2007 |
| 厦门 | 2003—2004 | 19 | 5.3 | 0 | 414 | 江天久等, 2007 |
| 浙江中南海域 | 2003—2004 | 12 | 9.1 | 306 | 胡颢琰等, 2006 | |
| 舟山海域 | 2003—2004 | 32 | 3.1 | 666 | 胡颢琰等, 2006 | |
| 上海市场 | 2003 | 66 | 0-30 | 1108 | Wu et al, 2005 | |
| 南麂列岛 | 2006—2007 | 60 | 11.7 | 0 | 461 | 吴锋等, 2010 |
| 东海* | 2006—2008 | 158 | 49.3 | 11.4 | 4240 | 梁玉波, 2012 |
| 东海 | 2006—2008 | 158 | 18.9 | 0.6 | 800 | 梁玉波, 2012 |
| 福建沿海 | 2007—2008 | 25 | 28 | 0 | 173 | 杜克梅等, 2013b |
| 东海* | 2013—2015 | 140 | 77.1 | 20 | 23793 | 本文 |
| 舟山市场 | 2015 | 60 | 15 | 0 | 540 | 何依娜等, 2016 |
| 福建沿岸 | 2017 | 23 | 56.5 | 43.5 | 34146 | 本文 |
| 平均值 | 24.8 | 8.9 | 11044 | |||
| 注: *为液相色谱法, 其他为小鼠生物法 | ||||||
1990年在广东贝类体中检出麻痹性贝类毒素(杨美兰等, 1999); 1998—2002年, 广东近海麻痹性贝类毒素污染比较严重, 1999年大亚湾扇贝消化腺中毒素含量可达227340µg/kg(江天久等, 2000a); 2003年至今, 南海近海麻痹性贝类毒素污染较轻(表 4)。
| 海域 | 年份 | 样本数(个) | 检出率(%) | 超标率(%) | 最高含量(µg/kg) | 参考文献 |
| 南海* | 1990—1991 | 3 | 100 | 100 | 7234.6 | Anderson et al, 1996 |
| 大亚湾 | 1990—1999 | 28 | 3513 | 杨美兰等, 1999, 2002 | ||
| 大鹏湾 | 1990—1999 | 25 | 2761 | 杨美兰等, 1999, 2002 | ||
| 珠江口 | 1990—1999 | 28 | 1742 | 杨美兰等, 1999, 2002 | ||
| 广东 | 1990—1992 | 90 | 35.5 | 2970 | 林燕棠等, 1994 | |
| 香港 | 1996—1998 | 5 | 80 | 20 | 3200* | Zhou et al, 1999 |
| 广东 | 1996 | 19 | 42.1 | 0 | 540 | 林燕棠等, 2001 |
| 广东 | 1997 | 22 | 27.2 | 0 | 760 | 林燕棠等, 2001 |
| 广东大亚湾* | 1998 | 6 | 100 | 100 | 10000 | 江天久等, 2000 |
| 广东 | 1999 | 35 | 17.1 | 0 | 648 | 林燕棠等, 2001 |
| 广东大亚湾 | 1998—1999 | 8 | 100 | 37.5 | 227340 | 江天久等, 2000a |
| 广东大鹏湾 | 1998—1999 | 8 | 100 | 25 | 1566 | 江天久等, 2000b |
| 广东* | 2001—2002 | 60 | 66.7 | 65 | 1116 | 吴施卫等, 2005a |
| 深圳 | 2002 | 30 | 33.3 | 3.3 | 918 | 江天久等, 2003 |
| 广东 | 2002—2003 | 22 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 杨美兰等, 2005 |
| 广西北海 | 2003—2004 | 22 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 江天久等, 2007 |
| 深圳 | 2003—2004 | 20 | 30 | 30 | 545 | 江天久等, 2007 |
| 广东 | 2005 | 10.8 | 0 | 356 | 吴施卫等, 2008 | |
| 广东大亚湾* | 2005—2006 | 4 | 100 | 0 | 383 | 冷科明等, 2014 |
| 广东大鹏湾* | 2005—2006 | 6 | 100 | 0 | 51.8 | 冷科明等, 2014 |
| 粤西* | 2005—2006 | 9 | 100 | 0 | 560 | 冷科明等, 2013 |
| 广东东部* | 2005—2006 | 10 | 100 | 20 | 1546 | 江天久等, 2010 |
| 南海* | 2006—2008 | 179 | 37.4 | 8.3 | 5096 | 梁玉波, 2012 |
| 南海 | 2006—2008 | 179 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 800 | 梁玉波, 2012 |
| 广东海域 | 2007—2008 | 118 | 25.4 | 0 | 463 | 杜克梅等, 2013a |
| 南海* | 2013—2015 | 133 | 47.3 | 9.8 | 2702 | 本文 |
| 平均值 | 53.4 | 20.6 | 10944 | |||
| 注: *为液相色谱法, 其他为小鼠生物法 | ||||||
2013—2015年, 全国近海麻痹性贝类毒素调查结果表明, 甲壳动物体中麻痹性贝类毒素污染最为严重, 消化腺中毒素可高达453154µg/kg, 超标率最高, 为22.2%;其次为棘皮动物, 超标率为16.7%;再次为软体动物, 超标率为16.5%;鱼类最低, 超标率为13.8%。春季超标率最高, 为24.8%;其次是冬季, 为20.8%;再次是夏季, 为14.4%;秋季最低, 为12.6%;不同海区有所差异, 如南海冬季毒素含量偏高。全国近海麻痹性贝类毒素超标率为17.4%, 其中北黄海、东海、南黄海、渤海、南海超标率依次为21.2%、20.0%、17.0%、15.6%和9.8%;在相对外海的海域, 如黄海獐子岛和威海, 东海枸杞岛, 南海三亚和东方等海域, 麻痹性贝类毒素含量明显偏高(图 1)。
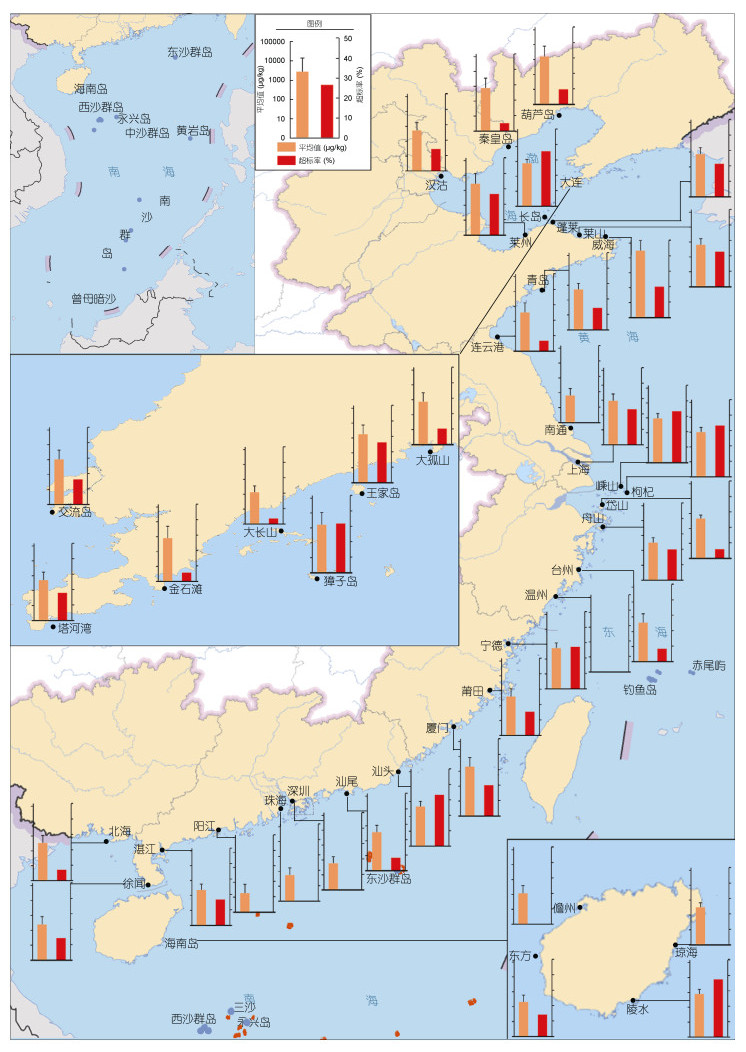 |
| 图 1 2013—2015年我国近海麻痹性贝类毒素污染状况分布图 Fig. 1 Map of paralytic shellfish poisoning (PSP) pollution in the coastal waters of China during 2013—2015 |
在我国近海发现产生麻痹性贝类毒素的常见微藻是亚历山大藻(Alexandrium spp.), 2002—2017年, 在全国近海形成24次赤潮(表 5)。仅凭普通光学显微镜观察是难以确定亚历山大藻种类的, 其中塔玛亚历山大藻研究报道的较多(Wang et al, 2005, 2008, 2011, 2014; Chen et al, 2013; Gu et al, 2013a)。根据5个不同的核糖体型, 塔玛亚历山大藻复合种已分为5个种:芬迪亚历山大藻(A. fundyense)(Ⅰ型)、地中海亚历山大藻(A. mediterraneum)(Ⅱ型)、塔玛亚历山大藻(A. tamarense)(Ⅲ型)、太平洋亚历山大藻(A. pacificum) (Ⅳ型)和澳洲亚历山大藻(A. australiense)(Ⅴ型)(John et al, 2014)。其中在黄渤海域是芬迪亚历山大藻, 长江口以南海域是太平洋亚历山大藻(Genovesi et al, 2015; Gao et al, 2015a, b)。此外, 在渤海发现了奥氏亚历山大藻(A. ostenfeldii), 在室内培养条件下, 不产生麻痹性贝类毒素C1/C2, GTX1-4(Gu, 2011), 但是可以产生STX和NEO (Gu et al, 2013a); 全球范围内, 一些地理种群的奥氏亚历山大藻还能产生spirolides等毒素(Kremp et al, 2014; Salgado et al, 2015)
| 起始时间 (年-月-日) |
结束时间 (年-月-日) |
最大面积 (km2) |
赤潮发生近海 | 优势种 |
| 2002-04-13 | 2002-04-15 | 80 | 福建宁德霞浦四礵列岛 | 夜光藻/塔玛亚历山大藻 |
| 2002-05-06 | 3.5 | 浙江岱山赤潮监控区 | 东海原甲藻/亚历山大藻 | |
| 2002-05-06 | 2002-05-11 | 800 | 浙江舟山虾峙门 | 东海原甲藻/亚历山大藻 |
| 2002-05-15 | 2002-05-26 | 100 | 浙江舟山嵊泗列岛 | 东海原甲藻/亚历山大藻 |
| 2003-04-28 | 30 | 浙江温州南麂上马鞍 | 东海原甲藻/亚历山大藻 | |
| 2003-04-28 | 2003-04-30 | 100 | 浙江舟山嵊泗列岛北部 | 东海原甲藻/亚历山大藻 |
| 2003-05-08 | 2003-05-12 | 3 | 浙江温州南麂三盘尾 | 东海原甲藻/亚历山大藻等 |
| 2003-05-15 | 2003-05-16 | 1 | 浙江温州南麂新码头 | 东海原甲藻/亚历山大藻等 |
| 2004-09-25 | 2004-10-04 | 172 | 辽宁大连金石滩海水浴场 | 亚历山大藻 |
| 2004-10-04 | 2004-10-11 | 2 | 辽宁大连老虎滩石槽村 | 亚历山大藻 |
| 2005-05-22 | 2005-05-25 | 浙江舟山虾峙岛东部 | 亚历山大藻 | |
| 2006-05-03 | 2006-05-08 | 1000 | 浙江舟山朱家尖东南 | 东海原甲藻/中肋骨条藻/米氏凯伦藻/亚历山大藻 |
| 2006-05-06 | 2006-05-12 | 10 | 浙江温州南麓大沙 | 三叶原甲藻/亚历山大藻 |
| 2006-09-14 | 2006-09-21 | 3 | 山东烟台长岛县南隍城乡 | 亚历山大藻 |
| 2007-09-25 | 2007-09-28 | 8 | 山东青岛沙子口湾 | 膝沟藻/亚历山大藻 |
| 2012-06-14 | 2012-06-18 | 80 | 浙江温岭石塘三蒜至钓滨 | 亚历山大藻/中肋骨条藻 |
| 2012-09-11 | 2012-09-13 | 40 | 辽宁大连龙王塘 | 亚历山大藻 |
| 2013-05-15 | 2013-0605 | 10.4 | 浙江温州洞头 | 东海原甲藻/亚历山大藻 |
| 2013-05-18 | 2013-06-02 | 120 | 浙江台州玉环坎门 | 东海原甲藻/亚历山大藻 |
| 2016-04-30 | 2016-05-04 | 4.5 | 河北秦皇岛 | 亚历山大藻/夜光藻 |
| 2016-08-01 | 2016-08-15 | 天津临港经济区 | 亚历山大藻 | |
| 2016-09-12 | 2016-10-24 | 630 | 天津渤海湾北部 | 伊姆裸甲藻/亚历山大藻 |
| 2017-07-20 | 2017-07-24 | 0.015 | 河北秦皇岛西浴场-金梦海湾 | 锥状斯克里普藻/海洋原甲藻/血红哈卡藻/亚历山大藻 |
| 2017-08-30 | 2017-09-04 | 37.8 | 广东汕尾后门港区及马宫港 | 锥状斯克里普藻/锥状斯克里普藻/亚历山大藻 |
| 注:数据来源于《中国海洋生态环境状况公报》(2003-2017) | ||||
链状裸甲藻(Gymnodinium catenatum)在我国近海可产生麻痹性贝类毒素(Gu et al, 2013b), 2005年至今, 已形成赤潮9次, 主要集中在渤海、江苏连云港和福建近海(表 6)。
| 起始时间(年-月-日) | 结束时间(年-月-日) | 最大面积(km2) | 赤潮发生近海 | 优势种 |
| 2005-10-29 | 2005-10-31 | 55 | 江苏连云港海州湾赤潮监控区 | 链状裸甲藻 |
| 2005-10-21 | 2005-10-23 | 200 | 江苏连云港海州湾赤潮监控区 | 链状裸甲藻 |
| 2006-01-02 | 2006-01-07 | 400 | 江苏连云港海州湾海域 | 短角弯角藻/链状裸甲藻 |
| 2007-08-21 | 2007-08-24 | 400 | 辽宁葫芦岛辽东湾芷锚湾 | 链状裸甲藻/柔弱伪菱形藻 |
| 2010-07-05 | 2010-07-07 | 100 | 江苏连云港海州湾海域 | 链状裸甲藻 |
| 2016-08-05 | 2016-08-15 | 2 | 天津临港经济区附近海域 | 链状裸甲藻 |
| 2017-05-17 | 2017-05-19 | 100 | 江苏连云港排淡河口至垺子河口 | 链状裸甲藻/中肋骨条藻 |
| 2017-06-06 | 2017-06-13 | 13.2 | 福建石狮、惠安 | 链状裸甲藻 |
| 2017-06-09 | 2017-06-12 | 40 | 福建龙海、漳浦佛昙 | 链状裸甲藻 |
| 注:数据来源《中国海洋生态环境状况公报》(2003-2017) | ||||
巴哈马梨甲藻(Pyrodinium bahamense)可产生麻痹性贝类毒素, 在南中国海(Usup et al, 2012)及香港海域均有分布(Dickman et al, 2002)。
1.3 麻痹性贝类毒素不同检测方法结果比较分析依据《食品安全国家标准贝类中麻痹性贝类毒素的测定》(中华人民共和国国家标准GB5009.213—2016), 我国现行麻痹性贝类毒素检测方法有:小鼠生物法、酶联免疫吸附法、液相色谱法、液相色谱-串联质谱法。小鼠生物法是测试所有麻痹性贝类毒素组分的毒性, 检出限低, 相当于300 μg STXeq/kg (Fernández et al, 1995; Bricelj et al, 1998), 难以确定毒素组分, 受测试动物的限制及检测程序繁琐, 不宜在基层监测单位推广应用。酶联免疫吸附法是应用检测试剂盒/试纸条, 可以快速、现场检测麻痹性贝类毒素, 既可定性又可定量, 易于在基层监测单位推广普及, 但目前国内外所有商品化麻痹性贝类毒素试剂盒/试纸条, 对麻痹性贝类毒素GTX1/4组分很少能检出(Jellett et al, 2002; 许道艳等, 2013; Harrison et al, 2016; Dorantes-Aranda et al, 2017), 而GTX1/4常常是海产品中的主要组分, 因此应用酶联免疫吸附检测麻痹性贝类毒素, 其检测结果会偏低。液相色谱法可确定已有13种参考标准物质的麻痹性贝类毒素组分, 其检测结果与小鼠生物法有着非常好的相关性, 但检测结果常常高出小鼠生物法(Wong et al, 2009), 可高出11.14%(江天久等, 2007)或49.36%(梁玉波, 2012)。这可能是小鼠生物法检测麻痹性贝类毒素的‘盐效应’及测试样品稀释比例不当所致(LeDoux et al, 2000), 毒素浓度可能被低估了60% (McFarren, 1959; Park et al, 1986)。由于液相色谱法检测麻痹性贝类毒素需要三种流动相检测程序, 十分繁琐, 现已逐渐被液相色谱-串联质谱法所取代, 液相色谱-串联质谱法检测灵敏度高, 操作简便(Zhuo et al, 2013; Mattarozzi et al, 2016; Shin et al, 2017), 其检测结果可高于小鼠生物法5—7倍(Li et al, 2012a)。
2 腹泻性贝类毒素或脂溶性海洋生物毒素污染状况及产毒微藻 2.1 我国近海腹泻性贝类毒素不同检测方法结果比较分析20世纪70年代, 美国官方分析化学师学会(Association of Official Agricultural Chemist, AOAC)推荐小鼠生物法为检测腹泻贝毒的标准方法, 并在全球范围内广泛推荐使用。本世纪初, 随着液相色谱-串联质谱等检测技术的发展, 发现小鼠生物法检测腹泻性贝类毒素假阳性问题十分严重, 从2015年起欧盟不再使用小鼠生物法检测腹泻性贝类毒素(EU, 2011), 将液相色谱-串联质谱法确定为腹泻性贝类毒素或脂溶性毒素检测的标准方法(EU et al, 2015)。依据《食品安全国家标准贝类中腹泻性贝类毒素的测定》(中华人民共和国国家标准GB5009.212—2016), 我国现行腹泻性贝类毒素检测方法有:小鼠生物法、酶联免疫吸附法、液相色谱-串联质谱法。从1993年至今, 应用小鼠生物法检测我国近海贝类体中腹泻性贝类毒素检出率/超标率为32.3%, 应用酶联免疫吸附法超标率9.2%, 应用液相色谱-串联质谱法超标率为5%(表 7)。比较上述三种方法可以看出, 小鼠生物法检测我国近海贝类体中腹泻性贝类毒素超标率高出酶联免疫吸附法3.5倍; 高出液相色谱-串联质谱法6.4倍。
| 检测方法 | 调查近岸海域范围 | 年份 | 样本数(个) | 检出率(%) | 超标率(%) | 参考文献 |
| 小鼠生物法 | 秦皇岛 | 1993—1994 | 53 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 李伟才等, 2000 |
| 秦皇岛 | 1995 | 65 | 21.5 | 21.5 | 李伟才等, 2000 | |
| 秦皇岛 | 1997 | 274 | 0 | 0 | 李伟才等, 2000 | |
| 青岛 | 1994—1996 | 805 | 5.6 | 5.6 | 李伟才等, 2000 | |
| 福建 | 1994—1996 | 146 | 4.8 | 4.8 | 李伟才等, 2000 | |
| 海南、广东、广西 | 2002—2004 | 55 | 56.4 | 56.4 | 吴施卫等, 2005b | |
| 上海市场 | 2003 | 66 | 22 | 22 | Wu et al, 2005 | |
| 广州市场 | 2004—2005 | 36 | 27.8 | 27.8 | 杨莉等, 2006 | |
| 广东近岸 | 2005 | 120 | 65 | 65 | 吴施卫等, 2008a, b | |
| 海南、广东、广西 | 2006 | 23 | 8.7 | 8.7 | 杨美兰等, 2009 | |
| 海南、广东、广西 | 2006—2008 | 179 | 68.7 | 68.7 | 梁玉波, 2012 | |
| 广东、广西 | 2007—2008 | 161 | 40.7 | 40.7 | 黄翔等, 2013 | |
| 深圳海域 | 2007—2008 | 168 | 10.1 | 10.1 | 黄海燕等, 2010 | |
| 珠江口、大亚湾 | 2008—2009 | 139 | 41 | 41 | 李嘉雯等, 2014 | |
| 海南 | 2010—2011 | 95 | 46.3 | 46.3 | 胡蓉等, 2013 | |
| 深圳市场 | 2011 | 64 | 18.8 | 18.8 | 王舟等, 2012 | |
| 长江口海域 | 2004—2005 | — | 12 | 12 | 王金辉等, 2007 | |
| 浙江、福建 | 2006—2008 | 158 | 60.1 | 60.1 | 梁玉波, 2012 | |
| 浙江 | 2007—2008 | 200 | 9.5 | 9.5 | 郑重莺等, 2012 | |
| 福建 | 2007—2008 | 13 | 54.5 | 54.5 | 黄翔等, 2013 | |
| 江苏、山东、辽宁 | 2006—2008 | 242 | 65.3 | 65.3 | 梁玉波, 2012 | |
| 江苏、山东、辽宁 | 2007—2008 | 61 | 44.3 | 44.3 | 黄翔等, 2013 | |
| 辽宁、河北、天津、山东 | 2006—2008 | 133 | 57.9 | 57.9 | 梁玉波, 2012 | |
| 平均值 | 32.3 | 32.3 | ||||
| 酶联免疫吸附法 | 深圳海域 | 2007—2008 | 168 | — | 14.9 | 黄海燕等, 2010 |
| 深圳市场 | 2011—2014 | 386 | — | 18.1 | 孙烨等, 2016 | |
| 深圳市场 | 2013—2014 | 186 | 100 | 12.9 | 潘柳波等, 2016 | |
| 宁波市场 | 2012 | 122 | 2.5 | 0 | 徐奋奋等, 2013 | |
| 江苏海州湾 | 2010—2012 | 42 | 80.4 | 0 | 宋向明等, 2013 | |
| 平均值 | 61 | 9.2 | ||||
| 液相色谱-串联质谱法 | 浙江 | 2009 | 40 | 22.5 | 17.5 | 张树刚等, 2001 |
| 浙江 | 2010 | 29 | 0 | 0 | 母清林等, 2013 | |
| 温州 | 2011 | 19 | 84.2 | 21.1 | 张秀尧等, 2012 | |
| 全国近海 | 2006—2007 | 76 | 34 | 0 | 刘仁沿等, 2014 | |
| 浙江 | 2007—2008 | 5 | 100 | 0 | 郑重莺等, 2012 | |
| 北黄海 | 2011 | 15 | 100 | 6.6 | 陈建华等, 2014 | |
| 广州市售 | 2012 | 60 | 11.7 | 0 | 李晓晶等, 2013 | |
| 广东 | 2012—2013 | 100 | 16 | 0 | 彭荣飞等, 2014 | |
| 福建省市售贝类 | 2013—2014 | 101 | 3.9 | 0 | 郑仁锦等, 2016 | |
| 平均值 | 41.4 | 5.0 | ||||
| 注: —表示没有数据 | ||||||
参照国际上以液相色谱-串联质谱法为检测腹泻性贝类毒素的标准方法, 可以看出小鼠生物法检测我国近海腹泻性贝类毒素假阳性问题十分严重, 应尽快废除。基层监测单位可应用酶联免疫吸附法的试剂盒/试纸条, 能检出腹泻性毒素主要组分OA和鳍藻毒素(dinophysistoxin, DTX), 酶联免疫吸附法的检测结果与液相色谱-串联质谱法一致率为79%—91%(刘仁沿等, 2008a, b; 刘丽等, 2016; Turner et al, 2016)。酶联免疫吸附法检出的超标样品, 再进行液相色谱-串联质谱法验证, 这样就可大幅度降低成本, 节省时间, 保证检测结果的可靠性。
2.2 我国近海脂溶性海洋生物毒素的污染状况腹泻性贝类毒素是脂溶性海洋生物毒素主要组成部分, 采用液相串联质谱法除了可检出腹泻性贝类毒素OA和DTX外, 我国近岸海域还能检出的其他海洋生物毒素有, AZA、蛤毒素组PTX、YTX、螺旋形亚胺(gymnodimine, GYM)、螺环内酯毒素(spirolides, SPX)、江瑶青毒素(pinnatoxins, PnTX)、(Pteriatoxin, PtTX)、prorocentrolide和spriocentrimine等。在黄渤海海水中, 全年可检出OA、DTX1、PTX2、YTX等毒素(Li et al, 2014; 宋新成等, 2016; 宿志伟等, 2017; Chen et al, 2017, 2018; Li et al, 2017)。在渤海(Liu et al, 2017b)和南海浮游生物体(Jiang et al, 2017; )中, 可检出OA、DTX1、PTX2、YTX、homo-YTX、AZA1、GYM等毒素。在黄海和东海海域沉积物中检出OA和PTX2毒素(Wang et al, 2015; Chen et al, 2017)。
在我国近海贝类体中, 常可检出OA、DTX1、PTX2、YTX、GYM、AZA1、AZA2、SPX1等毒素(刘仁沿等, 2008c, 2014; 高春蕾等, 2010; 姚建华等, 2010; Li et al, 2010, 2012b, 2017; Liu et al, 2011, 2017c; Jiang et al, 2017; Shen et al, 2018)。2000年至今, 我国近海仅有3起OA超出欧盟等国际限量标准160µg/kg的调查研究报道, 2000年大连的菲律宾蛤仔(Ruditapes philippinarum)体中OA最高含量为440µg/kg(傅云娜等, 2003); 2009年浙江南麂岛缢蛏(Sinonovacula constricta)体中OA最高含量为2770µg/kg, 贻贝(Mytilus edulis)体中最高含量为5850µg/kg, 泥蚶(Tegillarca granosa)体中最高含量为1060µg/kg(张树刚等, 2011); 2012年宁波和宁德贻贝(Mytilus galloprovincialis)体中最高含量为2111µg/ kg(Li et al, 2012b)。1997年连云港四角蛤蜊(Mactra veneriformis)中DTX1最高含量达160µg/kg(Zhou et al, 1999), 达到欧盟等国际限量标准160µg/kg。2011年大连虾夷扇贝(Patinopecten yessoensis)消化腺中YTX最高含量达6680µg/kg(陈建华等, 2014)和5667.5 ± 421.3µg/kg (Liu et al, 2017), 超出欧盟限量标准3750µg/kg。
2.3 我国近海产生脂溶性生物毒素的微藻在我国近海渐尖鳍藻(Dinophysis acuminata)等可产生OA、DTX1和PTX2等毒素(罗璇等, 2014; Li et al, 2015); 利玛原甲藻(Prorocentrum lima)可产生OA和DTX1毒素, 凯匹林纳原甲藻(Prorocentrum caipirignum)(Luo et al, 2017a)可产生OA毒素。慢原甲藻(Prorocentrum rhathymum)可产生OA等毒素(刘俏等, 2013, 勾玉晓等, 2018)。腹孔环胺藻(Azadinium poporum)可产生AZAs毒素(Gu et al, 2013c; Krock et al, 2014; Li et al, 2016; Luo et al, 2017b)。网状原角藻(Protoceratium reticulatum)可产生YTXs毒素(Liu et al, 2017)。SPX1可由奥氏亚历山大藻(Alexandrium ostenfeldii)产生(Salgado et al, 2015)。PnTX可由削廋伏尔甘藻(Vulcanodinium rugosum)产生(Selwood et al, 2014)。GYM在我国近海普遍检出, 鞍形凯伦藻(Karenia selliformis)可产生GYM(Mountfort et al, 2006), 但在我国近海至今尚未发现这一有毒微藻。
3 失忆性贝类毒素污染状况及产毒微藻失忆性贝类毒素的主要成分为软骨藻酸(domoic acid, DA)。依据《食品安全国家标准贝类中失忆性贝类毒素的测定》(中华人民共和国国家标准GB5009.198—2016), 失忆性贝类毒素的检测方法为:酶联免疫吸附法、液相色谱法和液相色谱-串联质谱法。用酶联免疫吸附法可快速检出海水、贝类、浮游植物样品中的软骨藻酸(许道艳等, 2007; 刘仁沿等, 2009; 王茜等, 2012; 刘淑娟等, 2014; 赵芮等, 2015)。用液相色谱法检测渤海14个水产动物样品, 50%检出软骨藻酸(陈西平等, 2001); 舟山附近海域贝类等水产品中检出率为64%(王恒, 2011); 南海栉孔扇贝和钝齿短桨蟹也能检出软骨藻酸(吉薇等, 2011)。用液相色谱-串联质谱法在浙江近海文蛤(宋琍琍等, 2008)和广东大亚湾浮游植物及海水可检出软海绵酸(Jiang et al, 2017)。此外, 用毛细管电泳法, 在大连近海栉孔扇贝体中检出软骨藻酸(李大志等, 2002)。上述所有调查结果表明, 我国近海虽能检出失忆性贝类毒素, 但均不超出欧盟等限量标准20mg/kg。
我国整个近海软骨藻酸产毒来源尚不清楚, 但从南海分离的拟菱形藻(Pseudo-nitzschia simulans)被证实可产软骨藻酸(Li et al, 2017)。
4 我国近海西加鱼毒素污染状况及产毒微藻根据分子结构及地域分布, 西加鱼毒素分为太平洋西加鱼毒素(Pacific ciguatoxin, P-CTXs)、加勒比海西加鱼毒素(Caribbean ciguatoxin, C-CTXs)及印度洋西加鱼毒素(Indian ciguatoxin, I-CTXs)。从小型草食性鱼类到高营养级肉食性鱼类都已检出西加鱼毒素。全世界每年约有50000—500000人受西加鱼中毒影响(Friedman et al, 2017)。依据《食品安全国家标准水产品中西加毒素的测定》(中华人民共和国国家标准GB 5009.274—2016), 西加鱼毒素的检测方法为小鼠生物法和液相色谱-串联质谱法。采用这两种方法, 2006—2008年, 我国南海近海西加鱼毒素超出欧盟等国际限量标准(0.1µg/kg)达17.4%(徐轶肖等, 2012)。2003—2013年香港市场鱼类体内西加鱼毒素检出率为85%(Wong et al, 2014)。
西加鱼毒素前驱物为冈比毒素(gambiertoxin), 由底栖甲藻冈比亚藻属(Gambierdiscus)产生。至今全世界共纪录14种冈比亚藻以及5种冈比亚藻基因型(Dai et al, 2017)。在我国近海已发现了3种冈比亚藻Gambierdiscus pacificus, G. australes 和G. caribaeus(Zhang et al, 2016), 但其毒素成分还没有报道。
5 结语(1) 麻痹性贝类毒素在我国近海污染十分严重, 基本呈现逐年加剧的趋势。20世纪九十年代, 南海麻痹性贝类毒素污染较重; 21世纪初, 北黄海麻痹性毒素污染较重; 近几年, 渤海和福建沿岸海域麻痹性贝类毒素污染较重。主要产毒微藻有亚历山大藻和链状裸甲藻。
(2) 采用小鼠生物法检测我国近海腹泻性贝类毒素超标率32.3%左右, 采用液相色谱/质谱法检测, 仅有3起腹泻性贝类毒素超标的研究报道; 现行小鼠生物法检测腹泻性贝类毒素假阳性问题十分突出, 应尽快废止。腹泻性贝类毒素均是脂溶性的, 脂溶性海洋生物毒素在我国近海常年可检出, 虾夷扇贝毒素和鳍藻毒素偶有超标现象。脂溶性海洋生物毒素产毒微藻有鳍藻和原甲藻及原角藻等。
(3) 失忆性贝类毒素在我国近海已常有检出, 但无超标现象。产毒藻为拟菱形藻等。
(4) 西加鱼毒素在我国南海污染较重, 但毒素标准物质的匮乏, 限制了我国对西加鱼毒素的调查研究。尚未确定产毒微藻种类。
(5) 藻毒素可先经酶联免疫吸附法检测, 需要验证的样品, 再经液相色谱-串联质谱法检测, 这样可大幅度降低成本, 缩短检测时间, 提高准确率, 已成为十分成熟配套的毒素检测技术。小鼠生物法检测毒素灵敏度低, 且受受试动物供应限制, 液相色谱法操作繁琐, 这两种方法已逐渐被淘汰。
于梅, 闫鹏, 徐景野. 2004. 宁波市1986~2003年织纹螺毒性检测结果分析. 实用预防医学, 11(6): 1267-1268 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-3110.2004.06.095 |
王舟, 黄薇, 潘柳波, 等. 2012. 2011年深圳市水产品卫生状况及风险评估. 中国公共卫生管理, 28(5): 595-597 |
王茜, 程金平, 高利利, 等. 2012. 软骨藻酸直接竞争ELISA方法的建立及优化. 环境科学, 33(2): 647-651 |
王恒. 2011. 舟山海域贝类海产品中软骨藻酸含量调查. 中国卫生检验杂志, 21(12): 2986-2988 |
王金辉, 秦玉涛, 刘材材, 等. 2007. 长江口及邻近海域有毒藻类和赤潮毒素的本底调查. 海洋湖沼通报, (1): 52-61 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1003-6482.2007.01.008 |
王雪虹, 黄世玉. 2007. 厦门海域养殖区麻痹性贝毒污染的研究. 集美大学学报(自然科学版), 12(2): 114-117 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-7405.2007.02.004 |
勾玉晓, 刘磊, 李冬梅, 等. 2018. 北黄海慢原甲藻形态结构与腹泻性贝类毒素组成. 中国渔业质量与标准, 8(3): 11-18 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.2095-1833.2018.03.002 |
孔凡洲, 徐子钧, 于仁成, 等. 2007. 黄渤海海域贝类麻痹性贝毒的检测与分析. 中国海洋大学学报, 37(2): 305-309 |
母清林, 王晓华, 佘运勇, 等. 2013. 浙江近岸海域贝类中重金属和贝毒污染状况研究. 海洋科学, 37(1): 87-91 |
吉薇, 郑洁莹, 曾雪萍, 等. 2011. 南海海域软骨藻酸(DA)贝类毒素的HPLC方法检测. 现代食品科技, 27(1): 120-122 |
刘丽, 刘磊, 赵芮, 等. 2016. 酶联免疫吸附分析检测鳍藻毒素DTX1和DTX2. 分析科学学报, 32(4): 557-560 |
刘俏, 龙丽娟. 2013. 南海慢原甲藻的培养和毒性初探. 湖北农业科学, 52(5): 1113-1117 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0439-8114.2013.05.034 |
刘仁沿, 许道艳, 董玉华, 等. 2009. 海水和贝类中软骨藻酸的酶联免疫吸附分析方法研究. 卫生研究, 38(5): 662-624 |
刘仁沿, 陈冰君, 梁玉波, 等. 2008a. 腹泻性贝毒软海绵酸单克隆抗体的制备和酶联免疫检测方法的建立. 卫生研究, 37(4): 443-445 |
刘仁沿, 高春蕾, 梁玉波, 等. 2008c. Gymnodimine, 首次在我国北海缘齿牡蛎中发现的一种腹泻性贝毒组分. 海洋学报, 30(6): 171-176 |
刘仁沿, 梁玉波, 刘磊, 等. 2014. 液相色谱结合串联质谱方法研究中国沿海贝类中脂溶性藻毒素的种类结构和分布规律. 生态环境学报, 23(8): 1320-1326 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2014.08.011 |
刘仁沿, 梁玉波, 陈冰君, 等. 2008b. 胶体金免疫层析方法快速检测腹泻性贝毒软海绵酸的初步研究. 分析试验室, 27(7): 26-29 |
刘淑娟, 赵晓祥, 程金平, 等. 2014. 快速检测软骨藻酸的间接ELISA方法. 环境科学学报, 34(2): 404-408 |
关春江, 冯志权, 马明辉, 等. 1999. 长江以北沿海经济贝类中的麻痹性贝毒. 海洋环境科学, 18(2): 49-52 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-6336.1999.02.010 |
江天久, 尹伊伟, 骆育敏, 等. 2000b. 广东大亚湾和大鹏湾麻痹性贝类毒素研究. 中国环境科学, 20(4): 341-344 |
江天久, 尹伊伟, 黄伟建, 等. 2000a. 深圳大亚湾麻痹性贝类毒素成分特征. 暨南大学学报(自然科学版), 21(5): 65-69 |
江天久, 包财, 雷芳, 等. 2010. 广东东部沿海麻痹性贝类毒素成分特征分析. 中国水产科学, 17(1): 119-127 |
江天久, 江涛. 2007. 中国沿海部分海域麻痹性贝毒研究. 海洋与湖沼, 38(1): 36-41 |
江天久, 陈菊芳, 邹迎麟, 等. 2003. 中国东海和南海有害赤潮高发区麻痹性贝毒素研究. 应用生态学报, 14(7): 1156-1160 DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2003.07.026 |
许道艳, 刘磊, 刘仁沿, 等. 2013. 麻痹性贝毒单克隆抗体的制备和酶联免疫检测方法的建立. 中国免疫学杂志, 29(1): 69-73 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-484X.2013.01.014 |
许道艳, 刘仁沿, 董玉华, 等. 2007. 失去记忆性贝毒ASP酶联免疫检测方法的研究. 海洋环境科学, 26(3): 237-240 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-6336.2007.03.009 |
孙烨, 刘威, 郑剑, 等. 2016. 2011-2014年深圳市贝类产品生物毒素污染状况调查. 检测研究, 28(2): 149-150 |
杜克梅, 江天久, 吴霓. 2013a. 黄海海域贝类麻痹性贝类毒素污染状况研究. 海洋环境科学, 32(2): 182-184 |
杜克梅, 雷芳, 吴霓, 等. 2013b. 我国东海和南海近岸海域麻痹性贝类毒素污染状况. 暨南大学学报(自然科学版), 34(3): 343-346 |
李大志, 祝文君, 朱文斌, 等. 2002. 记忆缺失性贝类毒素的主要成分--软骨藻酸的毛细管电泳分析. 色谱, 20(2): 125-128 DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1000-8713.2002.02.007 |
李伟才, 栾刚, 李立, 等. 2000. 中国沿海部分海区贝毒毒素的调查. 海洋科学, 24(9): 19-23 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-3096.2000.09.008 |
李晓晶, 彭荣飞, 于鸿, 等. 2013. 广州市市售水产品中多种脂溶性贝类毒素的监测. 中国卫生检验杂志, 23(10): 2317-2319 |
李嘉雯, 江涛, 吴锋, 等. 2014. 珠江口与大亚湾海域腹泻性贝毒污染状况分析. 暨南大学学报(自然科学与医学版), 35(3): 228-234 |
杨莉, 杨维东, 刘洁生, 等. 2006. 广州市售贝类麻痹性贝毒和腹泻性贝毒污染状况分析. 卫生研究, 35(4): 435-439 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-8020.2006.04.024 |
杨美兰, 林钦, 吕晓瑜, 等. 2005. 广东重要渔业水域牡蛎体中的麻痹性贝类毒素. 海洋环境科学, 24(1): 48-50 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-6336.2005.01.014 |
杨美兰, 林燕棠, 全桂英. 1999. 广东沿海牡蛎体的麻痹性毒素与评价. 湛江海洋大学学报, 19(3): 38-42 |
杨美兰, 林燕棠, 贾晓平, 等. 2002. 珠江口及邻近海域贝类麻痹性毒素调查. 中国水产科学, 9(3): 283-285 DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1005-8737.2002.03.022 |
杨美兰, 贾晓平, 林钦, 等. 2009. 南海海域重要养殖水域牡蛎体中的腹泻性贝类毒素. 海洋环境科学, 28(4): 410-413 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-6336.2009.04.014 |
吴锋, 江天久, 张帆, 等. 2010. 浙江南麂列岛海域贝类中的麻痹性贝类毒素研究. 海洋环境科学, 29(3): 360-363 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-6336.2010.03.016 |
吴施卫, 卢楚谦, 朱小山, 等. 2005a. 广东沿海麻痹性贝毒素的地理分布特征. 海洋环境科学, 24(3): 40-43 |
吴施卫, 张纯超, 卢楚谦, 等. 2005b. 南海近岸海域腹泻性贝类毒素分析. 海洋环境科学, 24(4): 48-51 |
吴施卫, 曾淼, 卢大鹏, 等. 2008a. 广东近岸海域2005年春季的腹泻性贝毒素特征分析. 海洋环境科学, 27(2): 165-168 |
吴施卫, 曾淼, 卢大鹏, 等. 2008b. 2005年春季广东近岸海域麻痹性贝毒素的特征分析. 海洋学研究, 26(4): 49-54 |
何依娜, 金雷, 梅光明, 等. 2016. 舟山市海水养殖贝类质量安全现状评价. 安徽农业科学, 44(27): 122-123 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2016.27.042 |
冷科明, 吴霓, 杜克梅, 等. 2013. 粤西海域麻痹性贝类毒素成分特征分析. 生态科学, 32(5): 558-563 |
冷科明, 吴霓, 杜克梅, 等. 2014. 粤中海域麻痹性贝类毒素成分特征分析. 海洋环境科学, 33(5): 666-671 |
宋向明, 谢小华, 赵冲厚, 等. 2013. 酶联免疫法测定牡蛎中腹泻性毒素的研究. 水产养殖, 34(1): 49-52 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-2091.2013.01.012 |
宋琍琍, 张海琪, 侯镜德, 等. 2008. 液相色谱-串联质谱法测定贝类毒素软骨藻酸的残留. 水产学报, 32(6): 950-956 |
宋普江, 张伟, 王刚, 等. 2011. 大连近岸海域经济贝类麻痹性贝毒分析. 海洋环境科学, 30(4): 533-535 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-6336.2011.04.018 |
宋新成, 周德山, 尹华斌, 等. 2016. 海州湾近海海域海水中贝类毒素的检测与季节变化. 淮海工学院学报(自然科学版), 25(3): 83-87 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-6685.2016.03.018 |
张秀尧, 蔡欣欣. 2012. 从暴发腹泻的贻贝中同时检出腹泻性贝类毒素和扇贝毒素. 中国卫生检验杂志, 22(8): 1905-1907 |
张树刚, 邹清, 陈雷, 等. 2011. 浙南海域腹泻性贝毒分析. 海洋科学, 35(1): 44-47 |
陈西平, 王成斌, 胡俊明, 等. 2001. HPLC方法检测水及水生动物中软骨藻酸. 卫生研究, 30(4): 247-248 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-8020.2001.04.022 |
陈建华, 于仁成, 孔凡洲, 等. 2014. 北黄海海域虾夷扇贝体内脂溶性藻毒素分析. 海洋与湖沼, 45(4): 855-863 |
林祥田, 张明生, 王志坚, 等. 2005. 连云港海州湾麻痹性贝类毒素中毒分析. 中国食品卫生杂志, 17(3): 243-246 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-8456.2005.03.011 |
林燕棠, 杨美兰, 陈瑞雯, 等. 1994. 广东沿海麻痹性贝类毒素的研究. 海洋与湖沼, 25(2): 220-225 |
林燕棠, 贾晓平, 杨美兰, 等. 1999. 中国沿岸染毒贝类的麻痹性毒素. 热带海洋, 18(1): 90-96 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.1999.01.014 |
林燕棠, 贾晓平, 杨美兰, 等. 2001. 我国海产贝类体中的麻痹性毒素及其来源. 水产学报, 25(5): 479-481 |
罗璇, 于仁成, 周名江. 2014. 应用LC-MS联用方法分析青岛近海渐尖鳍藻(Dinophysis acuminata)细胞中的毒素成分. 海洋环境科学, 33(5): 781-787 |
郑仁锦, 李榕珊, 黄宏南, 等. 2016. 福建省市售水产品中河豚毒素及腹泻性贝类毒素污染状况. 职业与健康, 32(17): 2367-2370 |
郑重莺, 张海琪, 宋琍琍, 等. 2012. 浙江省市售主要食用贝类中麻痹性贝类毒素和腹泻性贝类毒素污染状况分析. 浙江农业科学, (2): 236-239 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0528-9017.2012.02.042 |
赵芮, 刘磊, 刘丽, 等. 2015. 酶联免疫吸附法和液相色谱-质谱联用法分析海洋生物中记忆缺失性贝毒. 分析试验室, 34(8): 882-885 |
胡蓉, 江天久. 2013. 海南岛近岸海域贝类中的腹泻性贝类毒素. 暨南大学学报(自然科学版), 34(5): 527-532 |
胡颢琰, 唐静亮, 王益鸣, 等. 2006. 浙江近岸有害赤潮发生区麻痹性贝毒素研究. 海洋环境科学, 25(1): 63-65 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-6336.2006.01.018 |
姚建华, 谭志军, 周德庆, 等. 2010. 液相色谱-串联质谱法检测贝类产品中的原多甲藻酸贝类毒素. 色谱, 28(4): 363-367 |
夏远征, 王双双, 辛丘岩, 等. 2010. 大连海域贝类麻痹性贝毒的污染状况调查与分析. 食品与机械, 26(2): 54-56 |
徐奋奋, 吴蓓莉, 黄亚琴, 等. 2013. 宁波市市售海水产品腹泻性贝类毒素检测结果分析. 中国卫生检验杂志, 23(17): 3394-3395 |
徐轶肖, 王爱辉, 胡蓉, 等. 2012. 中国南部沿海近岸西加鱼毒素研究. 中国环境科学, 32(2): 330-336 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2012.02.021 |
高春蕾, 刘仁沿, 梁玉波, 等. 2010. 虾夷扇贝毒素yessotoxins(YTXs), 中国沿海贝类中首次发现的一组贝类生物毒素. 海洋学报, 32(3): 129-137 |
黄翔, 江天久, 吴霓. 2013a. 黄海海域贝类腹泻性贝类毒素污染状况研究. 海洋环境科学, 32(2): 178-181 |
黄翔, 雷芳, 江天久. 2013b. 我国东海和南海近岸海域腹泻性贝类毒素污染状况. 暨南大学学报(自然科学版), 34(1): 101-105 |
黄海燕, 黄爱君, 刘建军, 等. 2010. 深圳市海域贝类腹泻性毒素的污染状况分析. 中国卫生检验杂志, 20(3): 624-625 |
梁玉波. 2012. 中国赤潮灾害调查与评价(1933-2009). 北京: 海洋出版社, 543-659
|
宿志伟, 赵峰, 姜雪, 等. 2017. 桑沟湾养殖牡蛎中贝类毒素监测及预警. 食品科学, 38(6): 303-309 |
彭荣飞, 李晓晶, 于鸿, 等. 2014. 广东省经济贝类中多种贝类毒素的监测分析. 中国卫生检验杂志, 24(21): 3129-3131 |
韩华, 周春, 于光磊, 等. 2012. 大窑湾海域虾夷扇贝体内麻痹性贝毒的周年变化. 海洋环境科学, 31(3): 436-438 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-6336.2012.03.027 |
傅云娜, 陈则玲. 2003. 腹泻性贝毒的高效液相色谱法测定条件改进及其运用. 海洋通报, 22(1): 92-95 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2003.01.014 |
潘柳波, 黄薇, 王舟, 等. 2016. 深圳市市售贝类的腹泻性贝类毒素污染状况分析. 职业与健康, 32(5): 630-632 |
Anderson D M, Kulis D M, Qi Y Z et al, 1996. Paralytic shellfish poisoning in southern China. Toxicon, 34(5): 579-590 DOI:10.1016/0041-0101(95)00158-1 |
Bricelj V M, Shumway S E, 1998. Paralytic shellfish toxins in bivalve molluscs: Occurrence, transfer kinetics, and biotransformation. Reviews in Fisheries Science, 6(4): 315-383 DOI:10.1080/10641269891314294 |
Chen J H, Han T Z, Li X T et al, 2018. Occurrence and distribution of marine natural organic pollutants: Lipophilic marine algal toxins in the Yellow Sea and the Bohai Sea, China. Science of the Total Environment, 612: 931-939 DOI:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.08.304 |
Chen J H, Li X, Wang S et al, 2017. Screening of lipophilic marine toxins in marine aquaculture environment using liquid chromatographye-mass spectrometry. Chemosphere, 168: 32-40 DOI:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.10.052 |
Chen J H, Yu R C, Gao Y et al, 2013. Tracing the origin of paralytic shellfish toxins in scallop Patinopecten yessoensis in the northern Yellow Sea. Food Additives & Contaminants: Part A, 30(11): 1933-1945 |
Dai X F, Mak Y L, Lu C K et al, 2017. Taxonomic assignment of the benthic toxigenic dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus sp. type 6 as Gambierdiscus balechii (Dinophyceae), including its distribution and ciguatoxicity. Harmful Algae, 67: 107-118 DOI:10.1016/j.hal.2017.07.002 |
Dickman M, Tang S M, Lai J, 2002. A comparison of eastern and western Hong Kong Phytoplankton from weekly samples (1997-1999). Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 20(1): 52-61 DOI:10.1007/BF02846611 |
Ding L, Qiu J B, Li A F, 2017. Proposed biotransformation pathways for new metabolites of paralytic shellfish toxins based on field and experimental mussel samples. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 65(27): 5494 DOI:10.1021/acs.jafc.7b02101 |
Dorantes-Aranda J J, Campbell K, Bradbury A et al, 2017. Comparative performance of four immunological test kits for the detection of Paralytic Shellfish Toxins in Tasmanian shellfish. Toxicon, 125: 110-119 DOI:10.1016/j.toxicon.2016.11.262 |
E U, 2011. Commission Regulation N 15/2011 of 10 January 2011. Official Journal of the European Union, L6: 3-9 |
EU, European Union Reference Laboratory for Marine Biotoxins (EU-RL-MB), 2015. EU-Harmonised Standard Operating Procedure for determination of Lipophilic marine biotoxins in molluscs by LC-MS/MS. Version 5
|
Fernández M L, Cembella A D, 1995. Mammalian bioassays. In: Hallegraeff G M, Anderson D M, Cembella A D eds. Manual on Harmful Marine Microalgae. IOC Manuals and Guides. Paris: UNESCO, 33: 213-228
|
Friedman M A, Fernandez M, Backer L C et al, 2017. An updated review of ciguatera fish poisoning: clinical, epidemiological, environmental, and public health management. Marine Drugs, 15(3): 72 DOI:10.3390/md15030072 |
Gao H, An X, Liu L et al, 2017. Characterization of Dinophysis acuminata from the Yellow Sea, China, and its response to temperature and different Mesodinium prey. Oceanology Hydrobiology Study, 4(46): 439-450 |
Gao Y, Yu R C, Chen J H et al, 2015a. Distribution of Alexandrium fundyense and A. pacificum (Dinophyceae) in the Yellow Sea and Bohai Sea. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 96(1-2): 210-219 DOI:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.05.025 |
Gao Y, Yu R C, Murray S A et al, 2015b. High specificity of a quantitative PCR assay targeting a saxitoxin gene for monitoring toxic algae associated with paralytic shellfish toxins in the Yellow Sea. Applied Environmental Microbiology, 81(20): 6973-6981 DOI:10.1128/AEM.00417-15 |
Genovesi B, Berrebi P, Nagai S et al, 2015. Geographic structure evidenced in the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium pacificum Litaker (A. catenella–group IV (Whedon & Kofoid) Balech) along Japanese and Chinese coastal waters. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 98(1-2): 95-105 DOI:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.07.009 |
Gu H F, 2011. Morphology, phylogenetic position, and ecophysiology of Alexandrium ostenfeldii (Dinophyceae) from the Bohai Sea, China. Journal of Systematics and Evolution, 49(6): 606-616 DOI:10.1111/jse.2011.49.issue-6 |
Gu H F, Liu T T, Vale P et al, 2013b. Morphology, phylogeny and toxin profiles of Gymnodinium inusitatum sp. nov., Gymnodinium catenatum and Gymnodinium microreticulatum (Dinophyceae) from the Yellow Sea, China. Harmful Algae, 28: 97-107 DOI:10.1016/j.hal.2013.06.001 |
Gu H F, Luo Z H, Krock B et al, 2013c. Morphology, phylogeny and azaspiracid profile of Azadinium poporum (Dinophyceae) from the China Sea. Harmful Algae, 21-22: 64-75 DOI:10.1016/j.hal.2012.11.009 |
Gu H F, Zeng N, Liu T T et al, 2013a. Morphology, toxicity, and phylogeny of Alexandrium (Dinophyceae) species along the coast of China. Harmful Algae, 27: 68-81 DOI:10.1016/j.hal.2013.05.008 |
Harrison K, Johnson S, Turner A D, 2016. Application of rapid test kits for the determination of paralytic shellfish poisoning (PSP) toxins in bivalve molluscs from Great Britain. Toxicon, 119: 352-361 DOI:10.1016/j.toxicon.2016.06.019 |
Jellett J F, Roberts R L, Laycock M V et al, 2002. Detection of paralytic shellfish poisoning (PSP) toxins in shellfish tissue using MIST AlertTM, a new rapid test, in parallel with the regulatory AOAC® mouse bioassay. Toxicon, 40(10): 1407-1425 DOI:10.1016/S0041-0101(02)00153-8 |
Jiang T, Liu L, Li Y et al, 2017. Occurrence of marine algal toxins in oyster and phytoplankton samples in Daya Bay, South China Sea. Chemosphere, 183: 80-88 DOI:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.05.067 |
Jiang T, Xu Y X, Li Y et al, 2014. Seasonal dynamics of Alexandrium tamarense and occurrence of paralytic shellfish poisoning toxins in bivalves in Nanji Islands, East China Sea. Marine and Freshwater Research, 65(4): 350-358 DOI:10.1071/MF13001 |
John U, R. Litaker R W, Montresor M et al, 2014. Formal revision of the Alexandrium tamarense species complex (Dinophyceae) taxonomy: the introduction of five species with emphasis on molecular-based (rDNA) classification. Protist, 165(6): 779-804 DOI:10.1016/j.protis.2014.10.001 |
Krock B, Tillmann U, Witt M et al, 2014. Azaspiracid variability of Azadinium poporum (Dinophyceae) from the China Sea. Harmful Algae, 36: 22-28 DOI:10.1016/j.hal.2014.04.012 |
LeDoux M, Hall S, 2000. Proficiency testing of eight French Laboratories in using the AOAC mouse bioassay for paralytic shellfish poisoning: Interlaboratory collaborative study. Journal of AOAC International, 83(2): 305-310 |
Li Z X, Guo M M, Yang S G et al, 2010. Investigation of pectenotoxin profiles in the Yellow Sea (China) using a passive sampling technique. Marine Drugs, 8(4): 1263-1272 DOI:10.3390/md8041263 |
Li Y, Huang C X, Xu G S et al, 2017b. Pseudo-nitzschia simulans sp. nov. (Bacillariophyceae), the first domoic acid producer from Chinese waters. Harmful Algae, 67: 119-130 DOI:10.1016/j.hal.2017.06.008 |
Li A F, Jiang B Z, Chen H D et al, 2016. Growth and toxin production of Azadinium poporum strains in batch cultures under different nutrient conditions. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 127: 117-126 DOI:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.01.017 |
Li X, Li Z Y, Chen J H et al, 2014. Detection, occurrence and monthly variations of typical lipophilic marine toxins associated with diarrhetic shellfish poisoning in the coastal seawater of Qingdao City, China. Chemosphere, 111: 560-567 DOI:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.05.006 |
Li A, Ma J G, Cao J J et al, 2012a. Analysis of paralytic shellfish toxins and their metabolites in shellfish from the North Yellow Sea of China. Food Additives & Contaminants: Part A, 29(9): 1455-1464 |
Li A F, Ma J G, Cao J J et al, 2012b. Toxins in mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis) associated with diarrhetic shellfish poisoning episodes in China. Toxicon, 60(3): 420-425 DOI:10.1016/j.toxicon.2012.04.339 |
Li A F, Sun G, Qiu J B et al, 2015. Lipophilic shellfish toxins in Dinophysis caudata picked cells and in shellfish from the East China Sea. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22(4): 3116-3126 DOI:10.1007/s11356-014-3595-z |
Li M H, Sun G, Qiu J B et al, 2017. Occurrence and variation of lipophilic shellfish toxins in phytoplankton, shellfish and seawater samples from the aquaculture zone in the Yellow Sea, China. Toxicon, 127: 1-10 DOI:10.1016/j.toxicon.2016.12.009 |
Liu R Y, Liang Y B, Wu X L et al, 2011. First report on the detection of pectenotoxin groups in Chinese shellfish by LC–MS/MS. Toxicon, 57(7-8): 1000-1007 DOI:10.1016/j.toxicon.2011.04.002 |
Liu R Y, Liu L, Xu Y L et al, 2016. The production, distribution and fate of yessotoxins, taking the northern Yellow Sea of China for example. Environment and Ecology Research, 4(6): 322-345 DOI:10.13189/eer.2016.040605 |
Liu L, Wei N, Gou Y X et al, 2017. Seasonal variability of Protoceratium reticulatum and yessotoxins in Japanese scallop Patinopecten yessoensis in northern Yellow Sea of China. Toxicon, 139: 31-40 DOI:10.1016/j.toxicon.2017.09.015 |
Liu Y, Yu R C, Kong F Z et al, 2017a. Paralytic shellfish toxins in phytoplankton and shellfish samples collected from the Bohai Sea, China. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 115(1-2): 324-331 DOI:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.12.023 |
Liu Y, Yu R C, Kong F Z et al, 2017b. Lipophilic marine toxins discovered in the Bohai Sea using high performance liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry. Chemosphere, 183: 380-388 DOI:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.05.073 |
Luo Z H, Krock B, Mertens K N et al, 2017b. Adding new pieces to the Azadinium (Dinophyceae) diversity and biogeography puzzle: non-toxigenic Azadinium zhuanum sp. nov. from China, toxigenic A. poporum from the Mediterranean, and a non-toxigenic A. dalianense from the French Atlantic. Harmful Algae, 66: 65-78 DOI:10.1016/j.hal.2017.05.001 |
Luo Z H, Zhang H, Krock B et al, 2017a. Morphology, molecular phylogeny and okadaic acid production of epibenthic Prorocentrum (Dinophyceae) species from the northern South China Sea. Algal Research, 22: 14-30 DOI:10.1016/j.algal.2016.11.020 |
Mattarozzi M, Milioli M, Bianchi F et al, 2016. Optimization of a rapid QuEChERS sample treatment method for HILIC-MS2 analysis of paralytic shellfish poisoning (PSP) toxins in Mussels. Food Control, 60: 138-145 DOI:10.1016/j.foodcont.2015.07.027 |
McFarren E F, 1959. Report on collaborative studies of the bioassay for paralytic shellfish poison. Journal of the Association of Official Analytical Chemists, 42: 263-271 |
Mountfort D, Beuzenberg V, MacKenzie L et al, 2006. Enhancement of growth and gymnodimine production by the marine dinoflagellate, Karenia selliformis. Harmful Algae, 5(6): 658-664 DOI:10.1016/j.hal.2006.02.001 |
Park D L, Adams W N, Graham S L et al, 1986. Variability of mouse bioassay for determination of paralytic shellfish poisoning toxins. Journal of the Association of Official Analytical Chemists, 69(3): 547-550 |
Salgado P, Riobó P, Rodríguez F et al, 2015. Differences in the toxin profiles of Alexandrium ostenfeldii (Dinophyceae) strains isolated from different geographic origins: Evidence of paralytic toxin, spirolide, and gymnodimine. Toxicon, 103: 85-98 DOI:10.1016/j.toxicon.2015.06.015 |
Selwood A I, Wilkins A L, Munday R et al, 2014. Pinnatoxin H: a new pinnatoxin analogue from a South China Sea Vulcanodinium rugosum isolate. Tetrahedron Letters, 55(40): 5508-5510 DOI:10.1016/j.tetlet.2014.08.056 |
Shen H H, Chen J H, Xu X L et al, 2018. Development of a high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for determination of lipophilic toxins in marine shellfishes and edible safety evaluation. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 46(6): 985-992 DOI:10.1016/S1872-2040(18)61092-8 |
Shin C, Jang H, Jo H et al, 2017. Development and validation of an accurate and sensitive LC-ESI-MS/MS method for the simultaneous determination of paralytic shellfish poisoning toxins in shellfish and tunicate. Food Control, 77: 171-178 DOI:10.1016/j.foodcont.2017.02.034 |
Turner A D, Goya A B, 2016. Comparison of four rapid test kits for the detection of okadaic acid–group toxins in bivalve shellfish from Argentina. Food Control, 59: 829-840 DOI:10.1016/j.foodcont.2015.07.005 |
Usup G, Ahmad A, Matsuoka K et al, 2012. Biology, ecology and bloom dynamics of the toxic marine dinoflagellate Pyrodinium bahamense. Harmful Algae, 14: 301-312 DOI:10.1016/j.hal.2011.10.026 |
Wang Y L, Chen J H, Li Z Y et al, 2015. Determination of typical lipophilic marine toxins in marine sediments from three coastal bays of China using liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry after accelerated solvent extraction. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 101(2): 954-960 DOI:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.10.038 |
Wang D Z, Hsieh D P H, 2005. Growth and toxin production in batch cultures of a marine dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense HK9301 isolated from the South China Sea. Harmful Algae, 4(2): 401-410 DOI:10.1016/j.hal.2004.07.002 |
Wong C K, Hung P, Lee K L H et al, 2009. Effect of steam cooking on distribution of paralytic shellfish toxins in different tissue compartments of scallops Patinopecten yessoensis. Food Chemistry, 114(1): 72-80 DOI:10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.09.018 |
Wong C K, Hung P, Lo J Y C, 2014. Ciguatera fish poisoning in Hong Kong- A 10-year perspective on the class of ciguatoxins. Toxicon, 86: 96-106 DOI:10.1016/j.toxicon.2014.05.006 |
Wang D Z, Lin L, Gu H F et al, 2008. Comparative studies on morphology, ITS sequence and protein profile of Alexandrium tamarense and A. catenella isolated from the China Sea. Harmful Algae, 7(1): 106-113 DOI:10.1016/j.hal.2007.06.002 |
Wang Z H, Nie X P, Jiang S J et al, 2011. Source and profile of paralytic shellfish poisoning toxins in shellfish in Daya Bay, South China Sea. Marine Environmental Research, 72(1-2): 53-59 DOI:10.1016/j.marenvres.2011.04.007 |
Wang L, Zhuang Y Y, Zhang H et al, 2014. DNA barcoding species in Alexandrium tamarense complex using ITS and proposing designation of five species. Harmful Algae, 31: 100-113 DOI:10.1016/j.hal.2013.10.013 |
Wu J Y, Zheng L, Wang J H, 2005. Contamination of shellfish from Shanghai seafood markets with paralytic shellfish poisoning and diarrhetic shellfish poisoning toxins determined by mouse bioassay and HPLC. Food Additives & Contaminants, 22(7): 647-651 |
Zhang H, Wu Z, Cen J Y et al, 2016. First report of three benthic dinoflagellates, Gambierdiscus pacificus, G. australes and G. caribaeus (Dinophyceae), from Hainan Island, South China Sea. Phycological Research, 64(4): 259-273 DOI:10.1111/pre.12137 |
Zhuo L Y, Yin Y C, Fu W S et al, 2013. Determination of paralytic shellfish poisoning toxins by HILIC–MS/MS coupled with dispersive solid phase extraction. Food Chemistry, 137(1-4): 115-121 DOI:10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.10.010 |
Zhou M J, Li J, Luckas B et al, 1999. A recent shellfish toxin investigation in China. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 39(1-12): 331-334 DOI:10.1016/S0025-326X(99)00026-0 |
Zou C, Ye R M, Zheng J W et al, 2014. Molecular phylogeny and PSP toxin profile of the Alexandrium tamarense species complex along the coast of China. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 89(1-2): 209-219 DOI:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2014.09.056 |
 2019, Vol. 50
2019, Vol. 50

